Group Project 4 - Fully Pipelined MIPS
CS3410 Fall 2016
Work-in-progress Circuit Due: 11:59pm, Thursday, October 13, 2016,
Feedback will be given noon, Saturday, October 15, 2016
Final MIPS Circuit Due: 11:59pm, Wednesday, October 19, 2016
This is cumulative. Both Table A and Table B instructions are required.
You must work in the same group for this project as for the last.
Overview
In this project you will extend and complete the processor design you started in project 3. Your basic execution loop from the previous assignment should contain most of the major components, with the exception of RAM for the load/store instructions. For this project we will use a split-memory "Harvard" architecture design: The Program ROM will store a read-only copy of the instructions, and a separate RAM will be used to store data for the program's execution. You will now implement all the other instructions mentioned in the last project project, including load/stores, jumps and branches.
You should reuse most or all of your work from project 3. This means updating the circuit to handle the new instructions, revising the documentation to discuss any changes or addition to the datapath and control logic, and expanding your test program. This includes, of course, fixing anything that was broken or incomplete from project 3 (ask the staff for help if needed — we will not be posting a solution, but neither do we want to penalize you twice for mistakes in project 3).
Important: Consult the MIPS Handbook and make sure that all aspects of each of the instructions is implemented exactly as specified in the handbook, except where noted here.
Academic Integrity As one of the most widely studied architectures, MIPS has a wealth of information available on the web and in textbooks. You may consult any of the MIPS architecture documentation available to you in order to learn about the instruction set, what each instruction does, etc. But we expect your design to be entirely your own. If you are unsure if it is okay to borrow from some other source, just ask the TAs, and give credit in your final writeup. If you are unsure about asking the TAs, then it is probably not okay. Plagiarism in any form will not be tolerated.
What to Implement
Implement all of the instructions in Table B. You should have already decoded all these instructions in project 3. You may have to add additional decoding logic for any new control signals you introduce, as for the memory stage and for the PC update.
| Table B | |
| Jumps (with one delay slot) | J, JR, JAL, JALR |
| Branches (with one delay slot) | BEQ, BNE, BLEZ, BGTZ, BLTZ, BGEZ |
| Memory Load/Store (little endian, with pipeline stall if needed) | LW, LB, LBU, SW, SB |
Our testing programs will include a mixture of all the instructions from projects 3 and 4, so you must ensure that the instructions from project 3 are correctly implemented as well.
Deviation from the MIPS standard: You can ignore any MIPS instruction or feature not mentioned in this document, such as traps, exceptions, and system calls. You can also assume that your processor will never encounter anything but legal instructions from Tables A and B.
Refer to the MIPS manual, Volume 2, linked on the course web site for a full specification of what each of these operations does. Except where noted in here, the MIPS manual is the authoritative specification for this project: information you find elsewhere (e.g. Wikipedia or the book) doesn't count if it contradicts the MIPS manual.
JALR instruction. This is misleading. There is only one binary encoding for
the JALR instruction, and it is the version that takes two register arguments: JALR rd, rs. This is the
only one you have to implement. The alternate version of JALR, with rd omitted, is just an assembler
pseudo-instruction: whenever you write JALR rs, the assembler converts this to JALR $31, rs before it
encodes it in binary.Delay slot. You must properly implement the branch/jump delay slot, so that the instruction immediately following a branch or jump is always executed, and any relative addresses or significant bits for the PC update are based on the that address and not the address of the jump instruction itself.
Memory load hazard. Memory operations should not have delay slot, but instead use stalling to avoid hazards. That is, you should introduce a bubble in the pipeline after a memory operation, but only if a hazard is detected.
RAM. The "CS3410 Components" library in the most recent version of Logisim includes a MIPS
RAM component for your memory stage (see the description below). Logisim does not support RAM components large
enough to cover a full 32-bit (4GB) address space. The largest RAM component contains 64MB of data using 24-bit-wide
word-addresses. Our tests will rely on memory addresses in the lowest 1MB of the address space, so your your processor
should contain at least 1MB of RAM placed at the lowest addresses. That is, reads and writes to byte-addresses
in the range 0x00000000 to 0x000fffff should work as expected.
Important: Writes to addresses that not backed by any RAM should
have no effect, and the address space should not "wrap around" after 1MB.
For the adventurous. Instead of having a single RAM component backing the low part of the address space, you can add multiple RAM components to cover various convenient pieces of the address space. For instance, to support the conventional MIPS program layout, put a second RAM to cover a few MB of address space near addresses 0x10000000 for program data, and a third RAM to cover addresses just under 0x80000000 for the stack. Or you can redirect reads and writes at certain addresses to some of Logisim's input/output devices. It is actually fairly trivial to make writes at addresses just above 0x80000000 write coordinate and color pixel data to an LCD screen component or ASCII characters to a TTY component. Similarly you can make reads at some designated unused address read from a Logisim Keyboard, Joystick, or other input component. Bonus points if you can code pong to go with an LCD.
Restrictions and Naming Conventions
As in project 3, build your MIPS processor as a single Logisim circuit
file. Continue to use the components from the "CS3410 Components" library that
we provided.
Do not import circuits from other Logisim files.
Your top-level circuit must be named either "MIPS" or "MIPS32" (case-sensitive).
Your processor should have only one instance of each of these components: Register File, MIPS Program ROM, and ALU. The register file must be visible either in the toplevel circuit or one level down in a subcircuit. Do not nest the register file two more more levels down!
The restriction on incrementers and comparators has been relaxed since Project 3:
- You may now use more than one incrementer, although incrementing PC by 4 should still be done with one incrementer rather than four.
- You may use as many comparators as you like, however you will still be penalized for usages that are extremely inefficient.
You can additionally use any of the components that come with Logisim, such as a Register for the PC, multiplexers, and so on.
Testing
Write a test program in MIPS assembly that fully tests all of the features from both project 3 and project 4. As before, the program should be well commented, indicating what it is doing and what results should be expected when running the program, so that the course staff is convinced of the correctness of your processor.
We would also like you to test your program on a complex
computation. A hailstone sequence is defined as follows: start
at any positive integer n; if n is even, divide it by 2
to get n/2; else triple it and add one to get 3n+1; then
repeat with the new number. You will implement the hailstone
function, which counts how many steps it takes for the hailstone
sequence to converge to 1 from a given starting point. For instance,
hailstone(40) returns 8 because the sequence starting at
40 converges in 8 steps: 40, 20, 10, 5, 16, 8, 4, 2, 1. And
hailstone(31) returns 106 due to its long and chaotic
sequence: 31, 94, 47, 142, 71, 214, ..., 3077, 9232, 4616, 2308, 1154,
577, ..., 53, 160, 80, 40, 20, 10, 5, 16, 8, 4, 2, 1.
There are several ways to compute the hailstone function. You will implement all three of the methods below (please do not submit MIPS code with any form of main function). You should have already completed the iterative hailstone in Project 2 and the recursive hailstone in Lab 6
Iterative hailstone: An efficient approach for computing the answer for just a single sequence.
int i_hailstone(int n) { int i = 0; while (n != 1) { i = i + 1; if ((n % 2) == 0) n = n/2; else n = 3*n+1; } return i; }Recursive hailstone: Simple but inefficient. Logisim will be too slow to use this version except when the sequence converges quickly.
int r_hailstone(int n) { if (n == 1) return 0; else if ((n % 2) == 0) return 1 + r_hailstone(n/2); else return 1 + r_hailstone(3*n+1); }Memoization hailstone: For computing the answer for more than one sequence, it makes sense to remember previously computed answers since many sequences overlap. So if hailstone(40) has already been computed, then it is easy to compute hailstone(160) since its sequence is identical to the one for 40 after just 2 steps. This memoization version is essentially the same as the recursive version but takes two extra arguments: an array log_array of previously computed answers (should be initialized to all zeros), and the number of entries size in the array.
Note: the memoized hailstone does not allocate or initialize the array. It assumes that the function calling m_hailstone has already created an array of size size and initialized every entry to zero.
int m_hailstone(int n, int log_array[], int size) { if (n < size && log_array[n] != 0) /* non-zero means we already computed this */ return log_array[n]; if (n == 1) return 0; else { int i; if ((n % 2) == 0) i = 1 + m_hailstone(n/2, log_array, size); else i = 1 + m_hailstone(3*n+1, log_array, size); if (n < size) log_array[n] = i; /* save answer for reuse later */ return i; } }
Implement these three versions of the hailstone function using MIPS assembly code. They must all work on your processor in Logisim, though you will have be careful when testing to selecting starting values that converge in a reasonable time.
Your hailstone functions are just that: functions. They should get
their inputs from registers $a0 and $a1 and
they should return their results via register $v0. To
test the functions, you will nead to create a "main" program which
initializes the stack (by setting $sp
and $fp to something reasonable and usable), puts some
input in the argument registers, then calls the function
via JAL. The hailstone functions never make system calls
or any other function calls that could possibly read input from the
user. Your main program could if you managed to wire up a keyboard
though.
For the interested student: It is an open question whether all starting points eventually converge to 1 or not. Numbers that do converge are sometimes called wondrous numbers or hailstone numbers. The Collatz conjecture states that all positive integers are wondrous, but this isn't yet proven. For this project, you can assume all numbers converge — if you find one that doesn't you get an automatic A for the project. You can find links to more reading on the Wikipedia page for the Collatz conjecture.
Work-in-Progress Circuit
After receiving feedback on your mini-MIPS circuit from the previous project you will be required to submit a fixed, work-in-progress version.
The WIP circuit needs to address and fix all of the errors you had from P3, and should not have any extra functionality beyond what was previously required (i.e all Table B instructions should still be NOPs). We expect the work-in-progress circuit to work perfectly on P3 functionalities.
Your submitted work-in-progress circuit should be functional; i.e NO red wires, NO undefined outputs. Your WIP circuit will be tested on the same tests from P3.
Documentation
Document your design in the same fashion as project 3. Be sure to revise your block diagram to show any new components, and to revise your descriptions of control and instruction decoding logic to account for any changes or additions.
What to Submit
Note the different due dates
By Thursday, October 13, 2016
- Submit a work-in-progress version of your MIPS circuit on CMS
- Submit a README file stating what has and has not been implemented
By Wednesday, October 19, 2016
- A single Logisim project file containing your processor and all needed subcomponents.
- A PDF file documenting your processor, including a processor block diagram and description of control logic.
- A text file containing your well-commented MIPS assembly test program.
- Your iterative, recursive, and memoized hailstone implementations.
Help and Hints
MIPS calling conventions and program layout. The three versions of hailstone must be implemented as functions: they should take arguments and return results in registers (or on the stack), and use a call stack for recursive invocations. For this project, you are required to follow MIPS calling convention (as covered in class) precisely. You are expected to create these functions manually.
Fibonacci and other MIPS code online. A favorite assignment is implementing recursive, iterative, or memoizing Fibonacci functions. You can find MIPS implementations of this and much more online. GCC and other tools can also generate MIPS code for you. Feel free to use any online sources (but not from your classmates, obviously) by borrowing or adapting code as you see fit, or by using any other tool that is convenient for you. For instance, you might borrow function entry and exit code from an online example of Fibonacci, but replace the body with code for hailstone. Or you might obtain some of your test code by modifying the MIPS output of some compiler. In all cases: you must provide attribution by citing your sources, either in your documentation or directly in your code. And, you are ultimately responsible for what you turn in, so you had best understand everything you submit.
cs3410 Component Library Guide
The "CS3410 Components" library will only appear if you are using the most recent version of Logisim, downloaded from the course website. Please ensure that you are using the correct version. If so, you should have a folder in your sidebar containing the following components:
Using MIPS RAM as byte addressed and little endian RAM
For an in-depth guide of the RAM component: Click here
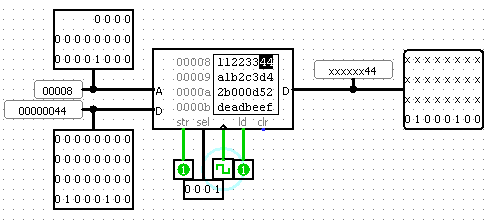
Here is a screenshot as I am writing the byte value 0x44 into byte address 32. Since the RAM is word addressed, this byte gets written to one of the four bytes at word address 32/4 = 8; you can see the A input to the RAM is 8. Since I want little-endian behavior, address 32 corresponds to the little end of the word (address 35 would be the big end of the same word, where 0x11 is stored); you can see the selector input is set to activate only the little end of the word. I am also reading at the same time, so you can see the 0x44 being read out on the litle end of the D output. If I were to activate all of the selectors, the RAM would output 0x11223344, which is the word stored at word address 8, i.e. byte address 4 * 8 = 32, which contains bytes 32 through 35.
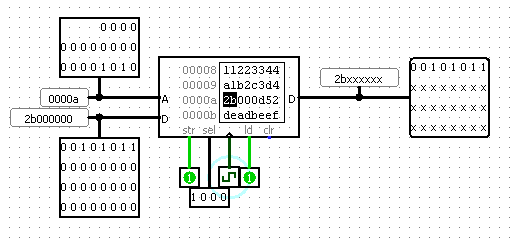
Here is another screenshot as I am writing the byte value 0x2b into byte address 43. Since the ram is word addressed, this byte gets written to one of the bytes at word address 43/4 = 10; you can see the A input to the RAM is 0xa = 10. Since I want little-endian behavior, address 43 corresponds to the big end of the word (address 40 would be the little end of the same word, where 0x52 is stored); you can see the selector input is set to activate only the big end of the word. I am also reading at the same time, so you can see the 0x2b being read out on the big end of the D output. If I were to activate all of the selectors, the RAM would output 0x2b000d52, which is the word stored at word address 0xa = 10, i.e. byte address 4 * 10 = 40, which contains bytes 40 through 43.
For writing byte 0xbb, depending on the address, I might want to put it at the big end, little end, or somewhere in the middle. Similarly for reading a byte, depending on the address, I might want to grab the bytes from the big end, little end, or somewhere in the middle. Hint: For writing, just direct the desired byte to all four positions then activate writing for just the one you want. For reading, you will need to select between the four possible positions where the byte might appear on the RAM's D output.
On the other hand, reading and writing whole words is trivial. The RAM is 32 bits wide, so just send the whole 32-bits to the memory, and read the whole 32-bits back to the CPU. You could try to be clever by swapping the order of each word's four bytes when writing to RAM, and un-swapping them when reading from RAM. This, however, would be entirely pointless. Can you tell why? Try it to see if it makes it any easier to read and write bytes.
|
Register File. A 32-bit wide by 32-registers deep register file. Register |
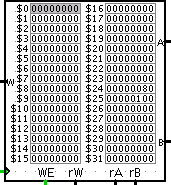 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
MIPS Program ROM. A 32-bit wide byte-addressed ROM, with built-in MIPS assembler. Use the attributes
panel to load a MIPS assembly file into the ROM. The |
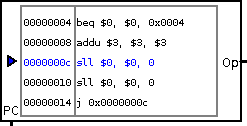 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
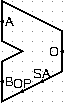
MIPS ALU. Computes a result as follows. You do not need to test the provided ALU, and can assume it will work exactly as specified.
|
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Incrementer. An adjustable-width incrementer. Takes its input |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
LCD Video. If |
 |
It is critical that your circuit adheres to the CS3410 Logisim Design Guidelines to avoid losing points!
MIPS (subset) Assembly Syntax
The MIPS Program ROM component has a built-in assembler that understands all of the instructions you will
implement. The syntax is standard MIPS syntax. Labels are case sensitive, everything else ignores case. Anything
following a pound ('#') is a comment. In project 1, you will only use a few of the instructions listed
here.
The instruction syntax is the same as given in the MIPS standard (and different from the output of gcc and
many other tools). Registers are written as $0, $1, ..., $31, and the destination register
goes on the left, followed by source registers and immediate values on the right. Most integer arguments (immediates,
shift amounts, jump targets) can be specified in hex (i.e. 0x12ab), in decimal (i.e. 1234 or -1234), a label, or the
special constant PC. The assembler will replace PC with the address of the instruction itself. Most
constants have some restrictions: jump destinations must have the same upper 4 bits as the PC+4, and must be
a multiple of 4; branch destinations must be a multiple of 4 and fit in a signed 18 bit immediate; etc. As a special case, when a branch
target is specified symbolically as a label, the assembler will automatically subtract the current PC value to obtain
a signed offset.
By default, the first instruction will be placed at address 0, and subsequent instructions are placed at at addresses 4, 8, 12, etc.
Assembler directives. The Program ROM assembler understands two standard MIPS assembler directives, .text and
.word, both of which take integer (hex or decimal) arguments. For example, .text 0x50000000 will
direct the assembler place subsequent instructions starting at address 0x50000000. And .word 0x24030005
directs the assembler to use the value 0x24030005 as the next machine instruction, which happens to be the machine
code for ADDIU $3, $0, 5.
Symbolic register names. The assembler built into the MIPS Program ROM accepts
standard MIPS register names: $zero, $at, $v0, $v1, $a0 - $a4, $s0 - $s7, $t0 -
$t9, $k0, $k1, $sp, $gp, $fp, and $ra.
Some examples of instructions are:
| Immediate Arithmetic | ADDIU $12, $0, PC |
| Register Arithmetic | ADDU $13, $0, $20 |
| Immediate Load | LUI $14, 0x123 |
| Shifts | SLL $13, $13, 2 SLLV $15, $14, $3 |
| Jumps | J 0x24 J my_label JR $5 JALR $31, $5 JALR $5 |
| Branches | BEQ $5, $6, -12 BEQ $5, $6, my_loop_top BLEZ $9, 16 BLEZ $9, my_loop_done |
| Memory Load/Store | LW $12, -4($30) SW $12, 0($30) |
MIPS (subset) Opcode Summary (from the MIPS Handbook)
Items in white are required for project 2. Make sure to implement all of them.
| opcode | bits 28..26 → | ||||||||
| ↓ bits 31..29 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | |
| 000 | 001 | 010 | 011 | 100 | 101 | 110 | 111 | ||
| 0 | 000 | SPECIAL δ | REGIMM δ | J | JAL | BEQ | BNE | BLEZ | BGTZ |
| 1 | 001 | ADDI | ADDIU | SLTI | SLTIU | ANDI | ORI | XORI | LUI |
| 2 | 010 | COP0 δ | COP1 δ | COP2 θδ | COP3 θδ | BEQL φ | BNEL φ | BLEZL φ | BGTZL Φ |
| 3 | 011 | β | β | β | β | SPECIAL2 δ | JALX ε | ε | * |
| 4 | 100 | LB | LH | LWL | LW | LBU | LHU | LWR | β |
| 5 | 101 | SB | SH | SWL | SW | β | β | SWR | CACHE |
| 6 | 110 | LL | LWC1 | LWC2 θ | PREF | β | LDC1 | LDC2 θ | β |
| 7 | 111 | SC | SWC1 | SWC2 θ | * | β | SDC1 | SDC2 θ | β |
| function | bits 2..0 → | ||||||||
| ↓ bits 5..3 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | |
| 000 | 001 | 010 | 011 | 100 | 101 | 110 | 111 | ||
| 0 | 000 | SLL | MOVCI δ | SRL | SRA | SLLV | * | SRLV | SRAV |
| 1 | 001 | JR | JALR | MOVZ | MOVN | SYSCALL | BREAK | * | SYNC |
| 2 | 010 | MFHI | MTHI | MFLO | MTLO | β | * | β | β |
| 3 | 011 | MULT | MULTU | DIV | DIVU | β | β | β | β |
| 4 | 100 | ADD | ADDU | SUB | SUBU | AND | OR | XOR | NOR |
| 5 | 101 | * | * | SLT | SLTU | β | β | β | β |
| 6 | 110 | TGE | TGEU | TLT | TLTU | TEQ | * | TNE | * |
| 7 | 111 | β | * | β | β | β | * | β | β |
| rt | bits 18..16 → | ||||||||
| ↓ bits 20..19 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | |
| 000 | 001 | 010 | 011 | 100 | 101 | 110 | 111 | ||
| 0 | 00 | BLTZ | BGEZ | BLTZL | BGEZL | * | * | * | * |
| 1 | 01 | TGEI | TGEIU | TLTI | TLTIU | TEQI | * | TNEI | * |
| 2 | 10 | BLTZAL | BGETAL | BLTZALL | BGETALL | * | * | * | * |
| 3 | 11 | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * |