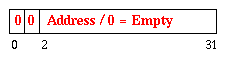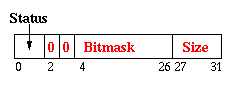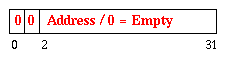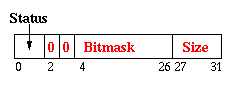| Type of Object | Header word format | Comments |
|---|
| Forwarded/Empty |
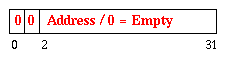 |
Assumes pointers are word aligned. So the bitmask represents a valid
address if/when we forward objects. We use an address of zero to represent
an empty header word.
|
| Small Record |
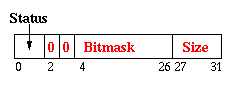 |
Bitmasks identify pointers in the object by 1's in the bitmask. Small
objects can have at most 22 words. |
| Large Record(Begin) |
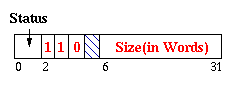 |
The beginning header word occurs adjacent to the object. Immediately
preceding it is the first bitmask word, whose bit 0 tells us whether the
first word of the object is a pointer or not.
|
| Large Record(End) |
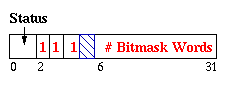 |
This header word marks the end of a sequence of bitmask words for a
large record. The top bits store the number of header words to facilitate
finding the beginning header word.
|
| Array |
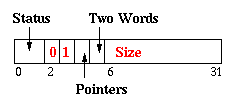 |
We support arrays that have either one word or two word elements, since
these are the only kind that occur in ML.
|
| Conservative Object |
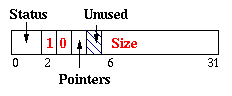 |
Conservative Objects are those for which no exact pointer information
is provided. However we allow the user to tell us whether the object has
pointers or not.
|