byte_set byteImage value
byte_set_with_mask byteImage bitMask value
Initialize all pixels in byteImage to value. The "with mask" form only copies where the corresponding pixel in bitMask is 1.
byte_set_mux_1 byteImage offset stride value
byte_set_mux_2 byteImage offset stride value
byte_set_mux_4 byteImage offset stride value
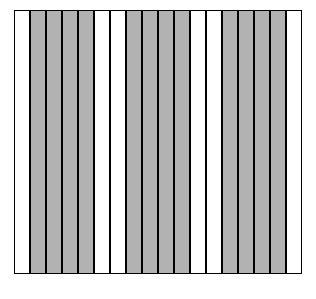
A ByteImage is divided into vertical strips, specified by three
parameters : length, offset and stride.
Length specifies the width of each strips. Offset
is the distance of the first byte of the first strip from
the first byte of each row in the ByteImage, and Stride
is the distance between the strips. For example, the figure below
shows the ByteImage with strips specified by length = 4, offset = 1,
and stride = 2.
byte_copy src dest
byte_copy_with_mask src bitMask dest
Copy the content of ByteImage src into ByteImage dest. The "with mask" form only copies where the corresponding pixel in bitMask is 1. The images must not overlap.
byte_copy_mux_1 src srcOffset srcStride dest destOffset destStride
byte_copy_mux_2 src srcOffset srcStride dest destOffset destStride
byte_copy_mux_4 src srcOffset srcStride dest destOffset destStride
These primitives copy the vertical strips of equal width from the src ByteImage into the dest ByteImage. The width of the strips is specified by the suffix of the primitives name. The offsets and strides are specified by the arguments to the primitives.
See the description of the byte_set_mux_1 primitive for a detail description of offset, stride and length.
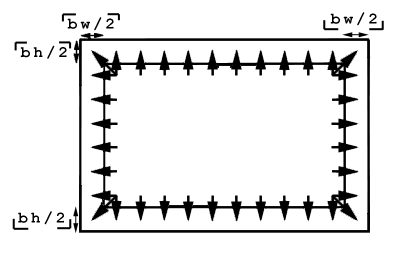
byte_extend byteImage bw bh
Fills borders (of total width bw and height bh) of byteImage by copying pixels from the interior as shown. This function can be used in conjunction with byte_clip and byte_copy to prepare an image for convolution.